Global System for Mobile Communications
GSM Introduction:
- GSM is the short form of Global System for Mobile Communications.
- It is called 2G or Second Generation technology.
- It is developed to make use of same subscriber units or mobile phone terminals throughout the world.
- There are various GSM standards such as GSM900, EGSM900, GSM1800 and GSM 1900; they mainly differ based on RF carrier frequency band and bandwidth.
GSM Network Architecture:
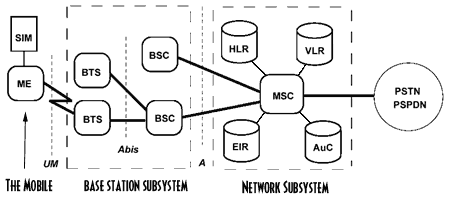
GSM network is consists of Mobile station, Base station subsystem and Network and operation subsystem. Following figure depicts complete GSM system network architecture.
Mobile Station– This Mobile station is GSM mobile phone equipment which houses DSP,RF chip and SIM(subscriber Identity Module). This SIM is enough to carry to avail the service of GSM network. SIM contains subscriber related all the information, network with which subscriber is subscribed with and encryption related information.
Base station Subsystem– Base station subsystem houses Base Transceiver station-BTS and Base station controller-BSC. This subsystem take care of radio control related functions and provides GSM air interface for GSM mobile phones to connect with GSM network. To provide GSM service, region/city on earth is divided into various cells. The cell size is usually about 100m to about 35 km. BTS coverage is limited to this cell. Like this many BTSs cover entire region. All this BTSs are interfaced with one BSC in various ways mesh, star etc. This BSC takes care of radio frequency assignments to the mobile phones, takes care of handoff within BSS i.e. between one BTS and the other BTS.
Network Subsystem (NSS) – This subsystem provides interface between cellular system and circuit switched telephone network i.e. PSTN. It performs switching and operation & maintenance related functions. NSS takes care of call processing functions such as call setup, switching, tear down and also hand over between BSCs. NSS takes care of security and authentication related functions. There are various network elements in this subsystem as mentioned in GSM network architecture above. They are explained below. These are basically database elements.
HLR-Home Location Register, it stores permanent and temporary subscriber related information.
VLR– Visitor Location Register, it stores visitor subscriber related information about its facilities, the network it is subscribed to, and its home location and so on.
AUC– Authentication centre, used to authenticate activities in the system. It holds encryption (A5 key) and authentication keys (A3 key)in both HLR and VLR.
EIR– Equipment Identification Register, it helps in security as it keeps track of equipment type available in Mobile Station or Terminal.
GSM Interface:
- Air interface between Mobile station and BTS
- Abis interface between BTS and BSC
- A interface between BSC and MSC
- SS7 interface between MSC and PSTN
- ReferGSM network interfaces page of gsm tutorial for detailed description.
GSM System Specification:
- Access Method- TDMA/FDMA
- Uplink frequency band- 890 to 915 MHz
- Downlink frequency band- 935 to 960 MHz
- System Bandwidth- 200KHz
- of frequency channels or ARFCN (Absolute Radio Frequency Channel Number)-124
- Users per channel-8
- Frame duration-4.615ms
- Spectral efficiency-1.35 b/s/Hz
- Data rate per user- 33.6 kbps (270.833 kbps Gross data rate for 8 users/8users)
