Code division multiple access
Code division multiple access (CDMA) is a channel access method used by various radio communication technologies.
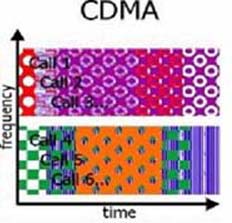
CDMA is an example of multiple access, where several transmitters can send information simultaneously over a single communication channel. This allows several users to share a band of frequencies. To permit this without undue interference between the users, CDMA employs spread-spectrum technology and a special coding scheme (where each transmitter is assigned a code).
Characteristics of code division multiple access:
- Spread spectrum techniques use a transmission bandwidth that is several orders of magnitude greater than the minimum required signal bandwidth. These systems were designed using spread spectrum because of its security and resistance to jamming.
- CDMA can effectively reject narrow band interference. Since narrow band interference affects only a small portion of the spread spectrum signal, it can easily be removed through notch filtering without much loss of information.
- CDMA devices use a rake receiver, which exploits multipath delay components to improve the performance of the system.
- In a CDMA system, the same frequency can be used in every cell, because channelization is done using the pseudo-random codes.
- Reusing the same frequency in every cell eliminates the need for frequency planning in a CDMA system;
- CDMA systems use the soft hand off, which is undetectable and provides a more reliable and higher quality signal.
General Specification of Code division multiple access
- Rx: 869-894MHz Tx: 824-849MHz
- 20 Channels spaced 1250kHz apart (798 users/channel)
- QPSK/(Offset) OQPSK modulation scheme
- 2288Mbps bit rate
- IS-95 standard
- Operates at both 800 and 1900 MHz frequency bands
Advantages of Code division multiple access techniques:
- Efficient practical utilization of fixed frequency spectrum.
- Flexible allocation of resources.
- Many users of CDMA use the same frequency, TDD or FDD may be used
Multipath fading may be substantially reduced because of large signal bandwidth
- No absolute limit on the number of users, Easy addition of more users.
- Impossible for hackers to decipher the code sentBetter signal quality
- No sense of handoff when changing cells
- The CDMA channel is nominally 1.23 MHz wide.
- CDMA networks use a scheme called soft handoff, which minimizes signal breakup as a handset passes from one cell to another.
- CDMA is compatible with other cellular technologies; this allows for nationwide roaming.
- The combination of digital and spread-spectrum modes supports several times as many signals per unit bandwidth as Analog modes.
Disadvantages to using Code division multiple access
- As the number of users increases, the overall quality of service decreases
- Self-jamming
- Near- Far- problem arises
Uses of CDMA:
- One of the early applications for code division multiplexing is in GPS. This predates and is distinct from its use in mobile phones.
- The Qualcomm standard IS-95, marketed as CDMA One.
- The Qualcomm standard IS-2000, known as CDMA2000. This standard is used by several mobile phone companies, including the globalstar satellite phone network.
- The UMTS 3G mobile phone standard, which uses W-CDMA.
- CDMA has been used in the OmniTRACS satellite system for transportation logistics.
Key elements of CDMA
CDMA is a form of spread spectrum transmission technology. It has a number of distinguishing features that are key to spread spectrum transmission technologies:
- Use of wide bandwidth:CDMA, like other spread spectrum technologies uses a wider bandwidth than would otherwise be needed for the transmission of the data. This results in a number of advantages including an increased immunity to interference or jamming, and multiple user access.
- Spreading codes used: In order to achieve the increased bandwidth, the data is spread by use of a code which is independent of the data.
- Level of security: In order to receive the data, the receiver must have a knowledge of the spreading code, without this it is not possible to decipher the transmitted data, and this gives a measure of security.
- Multiple access: The use of the spreading codes which are independent for each user along with synchronous reception allow multiple users to access the same channel simultaneously.
