Advanced Mobile Phone System
- (AMPS) is an Analog mobile cell phone system standard developed by Bell Labs, and officially introduced in Americas on October 13, 1983
- AMPS is a first generation cellular technology that uses separate frequencies or “channels”, for each conversation (Frequency-division multiple access (FDMA)).
- It therefore required considerable Bandwidth for a large number of users.
- In AMPS, the cell centres could flexibly assign channels to handsets based on signal strength, allowing the same frequency to be re-used in various location without interference.
- This allowed a larger number of phones to be supported over a geographical area.
- AMPS pioneers coined the term “cellular” because of its use of small hexagonal “cells” within a system.

AMPS Facts:
- Analog FM modulation
- The AMPS used 40MHz bandwidth and it used 800MHz band.
- RF bandwidth 30 kHz. The band can accomodate832 duplex channels , among which 21 are reserved for call setup, and the rest for voice communication.
- Frequency allocated by FCC on,
824-849MHz for downlink traffic
869-894MHz for uplink traffic
- Uses the same system throughout the US
- Available in U.S., Canada, Hong Kong, New Zealand, Thailand
- The AMPS was spread over 2100 square miles.
- The AMPS used frequency modulation and frequency division duplex(FDD) for radio transmission.
AMPS NETWORK LAYOUT:
The D-AMPS 800/1900 system architecture is similar to most other cellular system architectures. It contains a Switching System, an Operation and Support System, base stations and mobile station.
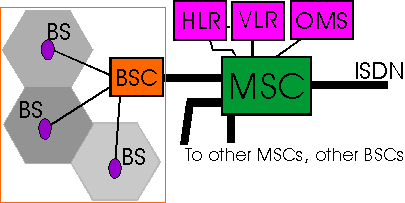
The switching system
The Switching System contains five main functional entities:
- The Mobile Switching Centre (MSC) performs the telephony switching functions for the network. It controls calls to and from other telephone and data communications networks such as Public Switched Telephone Networks (PSTN), Integrated Services Digital Networks (ISDN), Public Land Mobile Networks (PLMN) and Public Data Networks.
- The Visitor Location Register (VLR) database contains all temporary subscriber information needed by the MSC to serve visiting subscribers who are temporarily in the area of the MSC.
- The Home Location Register (HLR) database stores and manages user subscriptions. It contains all permanent subscriber information including the service profile, location information and activity status.
- The Authentication Centre (AC) supports authentication and encryption functionality. It verifies the user’s identity and ensures the confidentiality of each call (by encryption). This protects network operators against fraud.
- The Message Centre (MC) supports messaging services.
The base station
The Base Station is the radio equipment needed to serve each cell in the network. One base station site may serve more than one cell.
The Operation and Support System
The Operation and Support System supports operation and maintenance activities in the network to allow for reliable and cost-efficient operation.

