by admin | Jun 7, 2015 | sem3
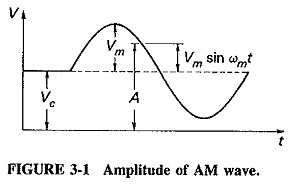
Amplitude Modulation Theory The process of changing the amplitude of the carrier signal in accordance with the modulating signal transmitted, keeping the frequency and phase of the carrier wave unchanged is known as amplitude modulation. Representation of AM wave: The...
by admin | Jun 7, 2015 | sem3
Needs for Modulation NEED FOR MODULATION 1) TO REDUCE THE ANTENNA HEIGHT 2) TO MULTIPLEX THE MORE NUMBER OF SIGNALS 3) TO REDUCE THE NOISE & DISTORTIONS 4) TO NARROW BANDING THE SIGNAL 5) TO REDUCE EQUIPMENT COMPLEXITY In simple terms, modulation is required to...
by admin | Jun 7, 2015 | sem3
TYPES OF MODULATION Based on the characteristics of the carrier signal, modulation can be classified as below: Amplitude Modulation. Frequency Modulation. Phase Modulation. THEORY OF AMPLITUDE MODULATION: The process of changing the amplitude of the carrier signal in...
by admin | Jun 7, 2015 | sem3
Modulation Modulation is the addition of information (or the signal) to an electronic or optical signal carrier. Modulation can be applied to direct current (mainly by turning it on and off), to alternating current, and to optical signals. One can think of blanket...
by admin | Jun 7, 2015 | sem3
Communication Systems In telecommunication, a communication systems is a collection of individual communications networks,transmission systems, relay stations, tributary stations, and data terminal equipment (DTE) usually capable of interconnection and inter operation...
by admin | Jun 7, 2015 | sem3
Noise Calculation noise calculation is the process of calculating the level of noise immission using the metric dB(A). Noise immission is created by noise sources (noise emission) of various types which are propagating noise into the environment. A single source will...


